Welcome to Yiwu Leifeng Electronic Technology Co., Ltd. website
Overview of Heat Transfer
Heat dissipation methods:
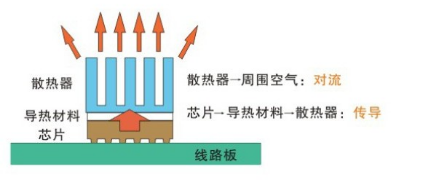
A: Conduction
B: Convection
C: Radiation
Thermal management is a key design challenge in next-generation products across the semiconductor, optoelectronics, consumer electronics, automotive, industrial, medical, and aerospace and defense sectors. The goal of modern electronic product thermal management is to effectively dissipate heat from the interface between the semiconductor and the surrounding environment.
Three main stages of heat transfer in electronic products:
Stage 1: Heat transfer within the semiconductor component package
Stage 2: Heat transfer from the package to the heat sink (initial heatsink)
Stage 3: Heat transfer from the heat sink to the ambient environment (final heatsink)
Stage 1 is not controllable by system thermal engineers, as the component type determines the internal heat transfer process. In stages 2 and 3, the goal of R&D engineers is to design effective connections from the surface to the initial heat sink and to the surroundings to achieve heat dissipation. This requires not only a comprehensive understanding of the fundamentals of heat transfer, but also knowledge of available interface materials and their important physical properties that affect the heat transfer process.
Yiwu Leifeng Electronic Technology Co., Ltd
Address: No.1, Huajin Road, Houzhai Industrial Zone, Yiwu City, Zhejiang Province
Telephone: +86-579-85680790
E-mail: sales@leifeng-tech.com
Fax: +86-579-85681397
Sorry,当前栏目暂无内容!
您可以查看其他栏目或返回 首页
Sorry,The current column has no content!
You can view other columns or return Home
